Make Your Chatbots GDPR Compliant
#chatbotsOnly one month left until the GDPR will take effect and people are already freaking out. If you haven't made yourself familiar with this topic, you need to do it now! This article will give you a summary of what you need to know and provide you with steps to make your chatbots GDPR compliant.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The GDPR will replace the Data Protection Directive in the European Union. It is designed to harmonize data privacy laws across Europe and will give more protection to individuals. It defines how E.U. citizens' data must be handled and will come into effect on the 25th of May 2018. It will affect businesses of all sizes and no matter where they are located. Everyone handling E.U. citizens' data will be bound to the GDPR's rules. Abuses will lead to big fines, which is why this topic should be taken very seriously.
Besides all the changes and efforts we are facing, it will help people to regain control over their personal data. The GDPR helps us to provide more data protection worldwide. This is a good thing and an essential step for everyone!
Key Changes
New Roles
Throughout the GDPR and this article, there are roles you need to know about:
- Data subject: a natural person whose personal data is processed by a controller or processor.
- Data controller: decides the purpose of the collected personal data.
- Data processor: processes on behalf of the Data Controller.
Increased Territorial Scope
The GDPR applies to all companies processing personal data of users, regardless of the companies location.
Penalties
Violating GDPR rules will lead to fines up to 4 percent of annual global turnover or €20 Million (which is greater).
Consent
Long and difficult to read terms and conditions are not valid anymore. Prior consent must be given in an accessible and easy form. Withdrawing consent must be as easy as giving it.
Personal Data Definition
Personal data means any information relating to a directly or indirectly identified or identifiable natural person. This includes any identifiers such as name, identification number, location data, email address, photo, bank details, medical information, posts on social networks, or IP address.
Data Subject Rights
- Right to get notified within 72 hours of a data breach.
- Right to gain access to the stored personal data.
- Right to be forgotten.
- Right to receive personal data in a readable format.
- Right to privacy by design and default.
Processing Personal Data
You are allowed to process personal data for the following reasons:
- User has given prior consent.
- Processing is necessary for the performance of a contract (e.g., store address to ship product).
- Processing is necessary for compliance with a legal obligation (e.g., accounting).
- Processing is necessary for the performance of a task carried out in the public interest (e.g., universities).
- Processing is necessary for vital interests (e.g., transferring medical data).
The GDPR distinguishes between the data controller and the data processor. The data controller determines the purpose and means of the processing of the personal data. The data processor processes this data. It becomes clearer after looking at an example.
On my blog, I collect emails for my personal newsletter. I use MailChimp to store the subscribers and to send out the newsletters. In this case, I am the data controller because I decide what to collect and what happens with the data. MailChimp is the data processor.
As a data controller, I need to make sure my data processors are GDPR compliant. This is done by a data processing agreement. Yeah, that's right. You need such an agreement for every one of your data processors. In the case of MailChimp, you can create such an agreement automatically on their site.
A lot of services you already use, will become your data processors. Here are a few examples:
- hosting provider (DigitalOcean, Linode, etc.)
- analytic tools (Google Analytics, etc.)
- email marketing tools (MailChimp, Campaign Monitor, etc.)
Confirm whether all of them are GDPR compliant. Most of these companies also already have agreements prepared for you. If you don't find any info on their websites, contact them.
Documentation
The accountability principle requires you to document that your organization processes personal information in line with the GDPR. Next, to the mentioned processor agreements, you need to maintain a record of processing activities. In addition to the mentioned processor agreements, you need to maintain a record of processing activities. This is true for controllers and processors. It forces you to write down what data you collect for which reasons and who you share it with. If there is an investigation, you will need to provide this information. This is the base making your business and projects GDPR compliant.
ePrivacy Regulation
There will also be a new ePrivacy regulation. It will replace the current ePrivacy Directive, also known as Cookie Law. Different from the GDPR, it will focus on how that personal data is used in the context of communication. We don't know yet when it will take effect, but you should be aware of it.
Back to Chatbots
These are some key facts about the upcoming GDPR. There is, of course, much more to this regulation, and you should check the official website for more details.
In general, GDPR for chatbots is very similar to any other application. It's about transparency, privacy, and taking personal user data seriously again.
11 Steps to Take
Here are the steps I recommend for making your chatbot GDPR compliant:
- Are you a business?
- Detrmine what data you're storing.
- Identify personal data.
- Are you allowed to process personal data?
- Use personal data for the agreed purpose only.
- Use data protection by default.
- Provide enough and precise information about used data.
- Give the user access to stored personal data.
- Give the user the possibility to delete stored personal data.
- Add a privacy policy.
- Make sure you don't log personal data.
Example
I am running a chatbot for my book Build Chatbots with PHP. It works as a messenger newsletter. The user can subscribe to get news on the book via Facebook Messenger. Let's work together through my steps to make it GDPR compliant.
1. Are you a business?
As noted already, the GDPR only affects businesses. So if you're a private person collection personal data from E.U. citizens for personal reasons only, you're done here and don't need the other steps.
I am a business, and the chatbot is also about a book I sell. So for me, it means the law will affect me and need to go on with the other steps.
2. Check What Data You're Storing
I am storing user information of everyone who is talking to the bot. These are the values that I store:
- Facebook Scoped ID
- First name
- Last name
- Profile picture URL
- Locale code
- Gender
3. Identify Personal Data
That's easy. All of the fields are personal data.
4. Are You Allowed to Process Personal Data?
We could argue, that it is evident that the chatbot needs personal data to send out messages. Still, this would only be a valid argument for the Facebook ID. It is better to assume we are not allowed yet. I also store personal data before asking the user about the subscription. If the user agrees, I set a flag to mark the user as a subscriber. That's a great example of how you shouldn't handle it.
5.Use personal data for the agreed purpose only
The chatbot asks its users before adding them as a subscriber. It then sends them news about the book via Facebook messenger. The personal data is not used for anything else.
6. Use data protection by default
There is data protection by default and by design. By Design means we should think about data protection from the very beginning of a project. By Default means we should ensure that default settings should have the highest possible data privacy. It also means you shouldn't save any information you do not need.
Actually, I only need the user's name and the Facebook ID to send out messages. The other fields are not relevant to the use-case. As mentioned, I also store information about users even if they don't subscribe. That is not valid anymore, because there is no communicated purpose and no consent. I need to change my chatbot to only store the minimum of data required for sending out messages and only to store them for subscribed users.
7. Provide Enough and Clear Information About Used Data
Here is the information the chatbot provides about the subscription and usage of data.
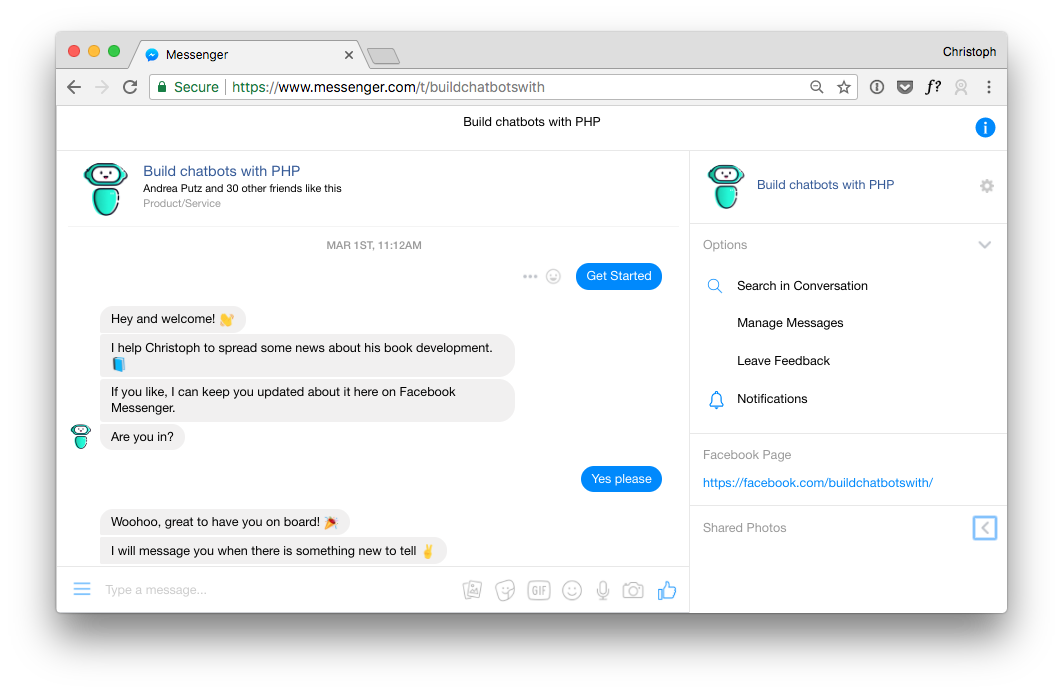
Apparently, the bot is not telling enough. I need to update this section to give users a better insight into what is happening. It must be obvious what they are subscribing to and what personal data is being used. You also need to mention the privacy policy.
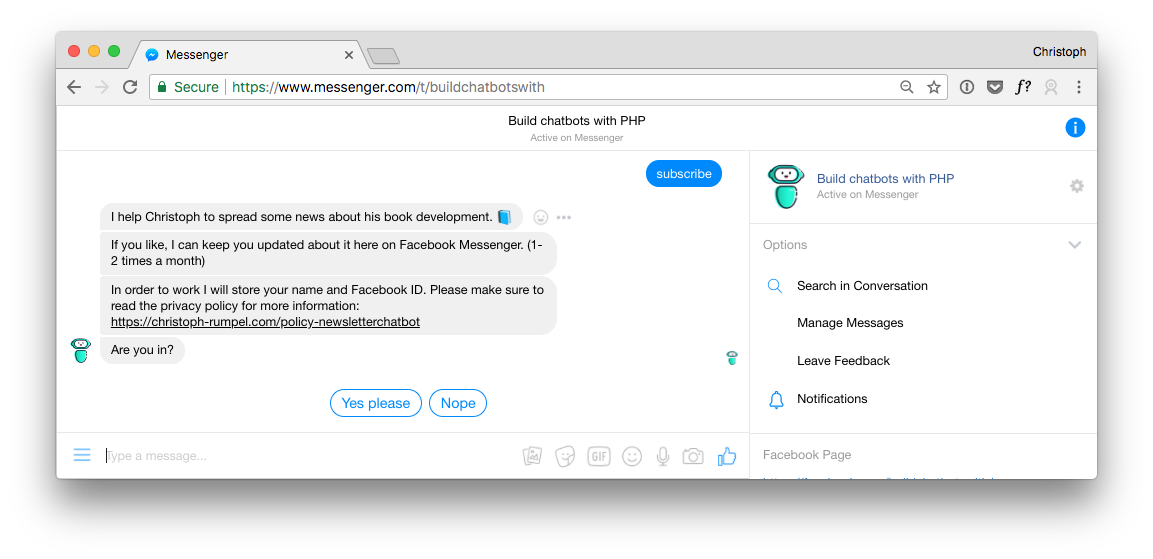
8. Give the User Access to Stored Personal Data
My chatbot was missing a feature to show stored personal data. This is why I added a new section in the menu. It is now easy for the user to see the stored data.
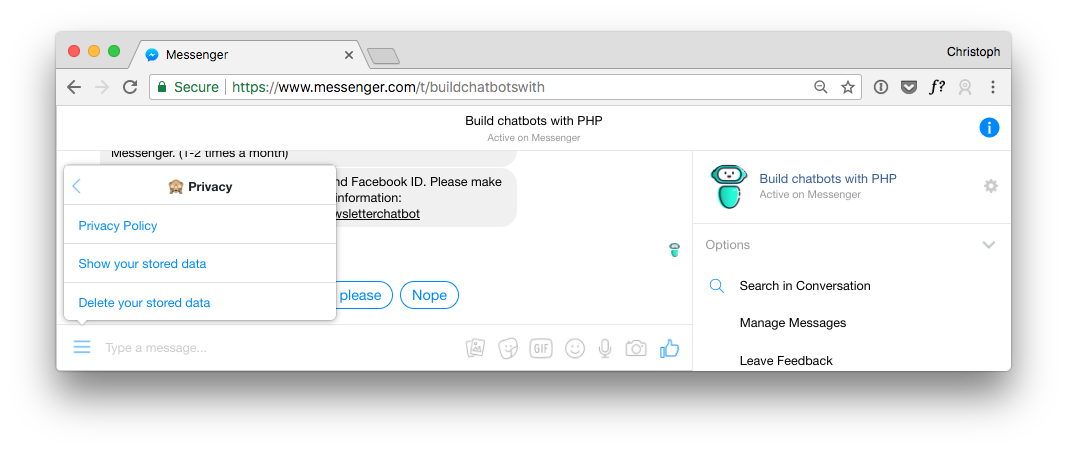
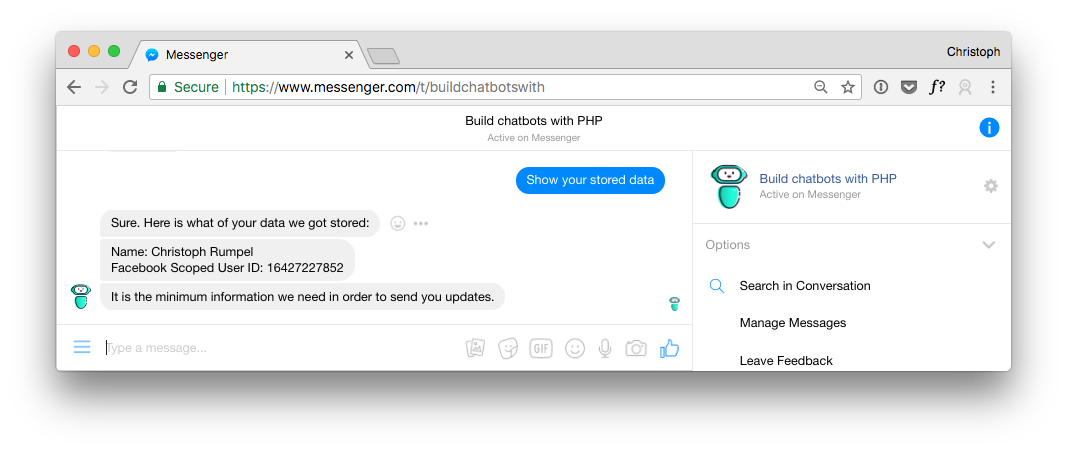
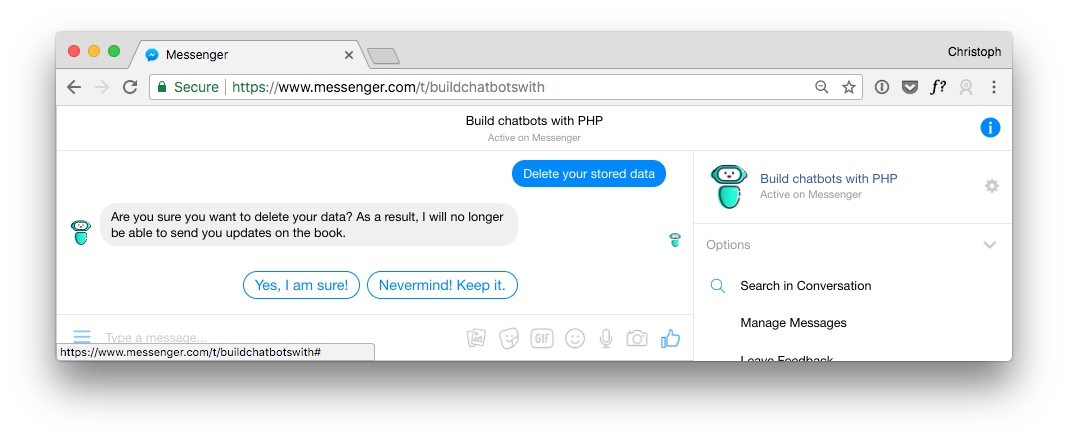
9. Give the User the Possibility to Delete Stored Personal Data
The same goes for the right to be forgotten. In the menu is another option to let the user delete its data.
10. Add a privacy policy
GDPR requires all companies operating in the EU to have a privacy policy. It should contain:
- What information is collected?
- Who collects it?
- Why is it collected?
- How long will it be used?
- Who will it be shared with?
- How can I withdraw?
You need to let users know about this policy before collecting personal data. As you have seen, I provide a link to it within the subscription information. Additionally, there is also a new menu link to the updated privacy policy.

11. Be Careful with Server Logs
While working with chatbots, it is common to log incoming requests from messenger services like Facebook or Telegram. They help a lot while debugging, but they contain personal data like IDs, messages, and names. You are not allowed to store them without prior consent or the mentioned permitted reasons. I only turn them on for debugging purposes now
The same goes for general server logs. They often contain IPs and other personal data like usernames from the URL. Here people discuss if they are mandatory for securing the access to the application. This would be a valid reason to store them. But, then you need to make sure to mention this in your privacy policy, as well as taking care of deleting them as soon as possible.
Conclusion
The General Data Protection Regulation brings a lot of changes to the web. It is an complex topic, and you need to take some time to make yourself familiar with. Everybody is trying right now to make their products GDPR compliant and as you have seen it is not that easy and clear what it takes. I hope this article could help you to get a better understanding of this new regulation and what it means for your chatbots.
This article focused on the project side of GDPR. Please keep in mind that there is much more for you or your company to consider to fulfill the GDPR.